Titanium Dioxide in Confectionery
Titanium dioxide, a fine, white powder, is ideal as a balancer for edible pigments because of its excellent properties for reflecting light. TiO2 generates opacity that is unmatched for food pigments, enabling a wide range of bright colors. This is why it’s a common additive for baking and candy -making products. In addition, titanium dioxide’s high level of opacity to both visible and ultraviolet light helps protect food, beverages, medications, and cosmetics from degrading, which prolongs the shelf life of products.
Titanium dioxide’s opacity makes it a uniquely useful ingredient to cover dark or non-uniform centers in confectionery and nutritional supplements. Its whiteness is a pure canvas for confectionery coloring and designs, serving as a base for a wide variety of color palettes, from pastel to bright and from dark to light. It also acts as a universal balancer, allowing for distinctive custom colors to be created to support brand recognition in marketing.
The Safety of Titanium Dioxide
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has assessed the safety of titanium dioxide pigment as a color additive in food, drug, and cosmetic applications and found it to be safe for ingestion and as a skin applicant. In March 2020, however, Europe’s food safety regulator, EFSA, updated its safety assessment of titanium dioxide and banned it for use as a food additive in the European Union. This has led some consumers and companies in the U.S. to question its safety.
EFSA’s decision was based on uncertainty about potential genotoxicity after long-term consumption of titanium dioxide, which may cause the substance to accumulate in the body. It’s important to note that the studies used by EFSA – which were part of a broader concern about the unknown accumulation of nanoparticles in the body -- for its decision do not find a link to genotoxicity. However, the agency found that it could not definitively eliminate the possibility. More importantly, the studies used by the European agency on general and organ toxicity did not indicate evidence of any adverse effects on human health.
In response to ESFA’s decision, the U.S. FDA reviewed the data that prompted the EU to ban titanium dioxide in food products in Europe and noted that it takes a different view on interpreting the research.
In addition, Health Canada issued a statement in June of 2022 reaffirming its opinion that “there is no conclusive scientific evidence that the food additive TiO2 is a concern for human health,” following a comprehensive review of the research used by ESFA. Health Canada further noted that many studies that raised safety concerns about titanium dioxide as a food additive used forms of TiO2 “that are not considered acceptable for use in food and have different properties than food-grade TiO2.”
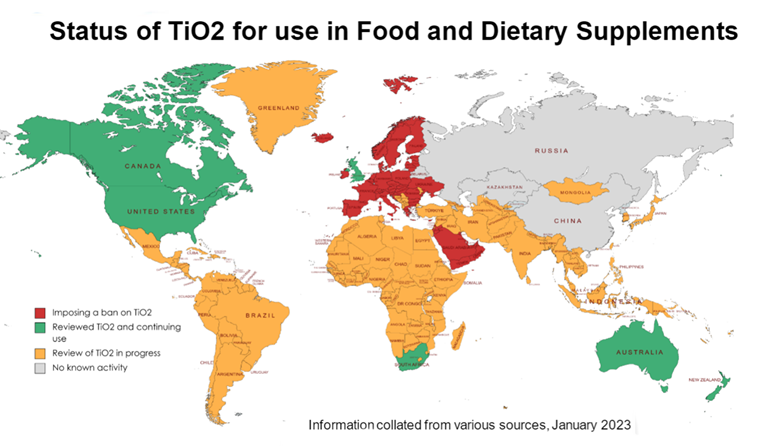
A disconnect between interpretations of food safety studies between the United States and the European Union is not unusual. In fact, the EU allows for the inclusion of ingredients in food products that are banned in the United States, including vegetable carbon black, a type of dye produced by the carbonization (charring) of organic materials such as wood, shells (including coconut) and peat.
The Difficulties in Eliminating Titanium Dioxide from Confectionery
Some confectionery companies have attempted to move away from using titanium dioxide due to its somewhat controversial reputation. These products can tend to be duller in color, more uneven looking, and less pleasing to the eye. Achieving bright, eye-catching colors without an opacified white foundation is virtually impossible.
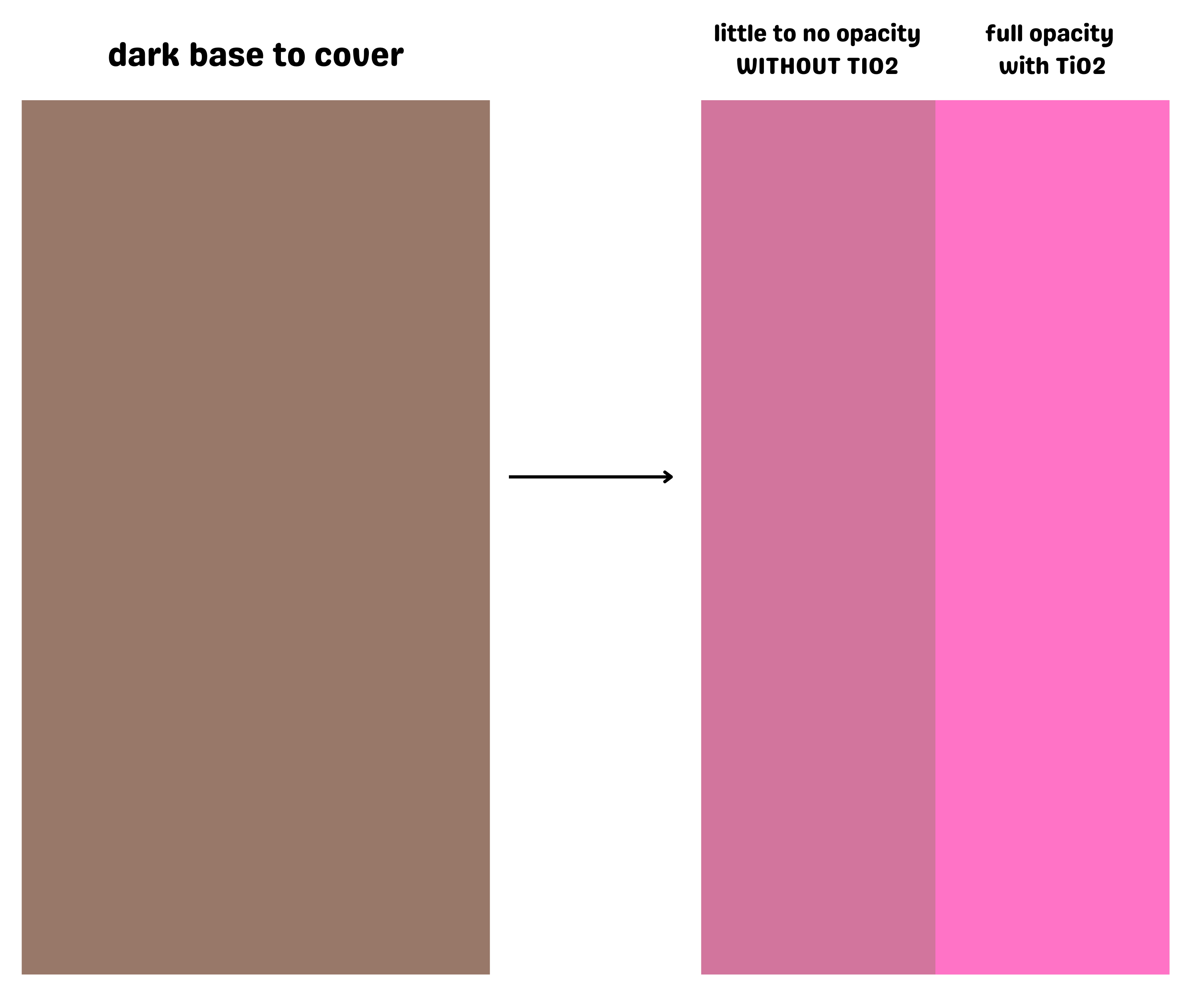 It helps to consider the widespread use in paint to grasp the difficulty of eliminating titanium dioxide. If you have ever tried to paint a dark wall a lighter color, you’ll know that without an opaque white base coat, your new- more translucent- light color won’t achieve the coverage you expect. The dark color from below will show through and mute the color you’re targeting.
It helps to consider the widespread use in paint to grasp the difficulty of eliminating titanium dioxide. If you have ever tried to paint a dark wall a lighter color, you’ll know that without an opaque white base coat, your new- more translucent- light color won’t achieve the coverage you expect. The dark color from below will show through and mute the color you’re targeting.
The same situation occurs in the world of confectionery as well, particularly when it is required to cover darker ingredients such as chocolate. Simply put, no other FDA food-approved white alternatives have the opacity power that titanium dioxide possesses.
TiO2 and Non-TiO2 Colorant Options
At Colorcon Specialty Markets, we take food safety seriously and frequently provide custom reformulations when you need them in response to customer concerns or regulatory guidance. While we can work together on reformulation options, it’s important to understand the complexities and hurdles you’ll endure when taking on this challenge. Let our Technical Service Team help guide you through the intricacies of these modifications.
Interested in learning more about titanium dioxide and non-titanium dioxide colorant options? Contact us today.


 It helps to consider the widespread use in paint to grasp the difficulty of eliminating titanium dioxide. If you have ever tried to paint a dark wall a lighter color, you’ll know that without an opaque white base coat, your new- more translucent- light color won’t achieve the coverage you expect. The dark color from below will show through and mute the color you’re targeting.
It helps to consider the widespread use in paint to grasp the difficulty of eliminating titanium dioxide. If you have ever tried to paint a dark wall a lighter color, you’ll know that without an opaque white base coat, your new- more translucent- light color won’t achieve the coverage you expect. The dark color from below will show through and mute the color you’re targeting.